Dips are a staple in many workout routines, renowned for their ability to build strength and muscle in the upper body. But what muscles do dips work exactly? Understanding the muscle groups targeted by dips can help individuals optimize their workouts and ensure they are achieving their fitness goals. This in-depth analysis will explore the primary and secondary muscles engaged during dips, discuss various dip variations, and offer insights on how to incorporate this effective exercise into any fitness regimen.
Primary Muscles Engaged in Dips
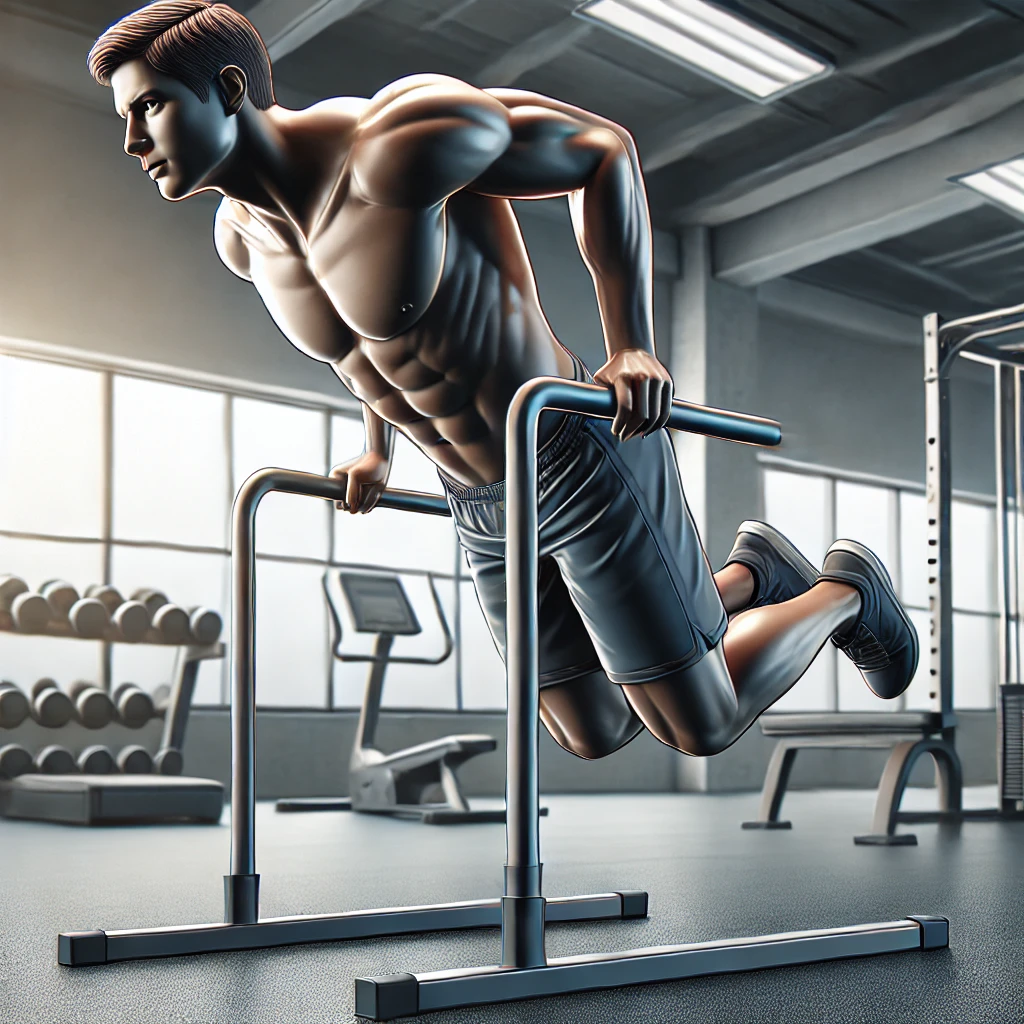

The primary muscles targeted during dips are the triceps brachii, situated on the back of the upper arms. These muscles are crucial for elbow extension, a key movement when performing dips. As one pushes the body upward, the triceps are directly engaged. Additionally, the chest muscles, particularly the pectoralis major, play a significant role. When the body is lowered and raised, the chest muscles contract to assist with the movement and stabilization. This combined action of the triceps and chest muscles makes dips highly effective for building upper body strength and muscle definition.
Secondary Muscles and Stabilizers

While the triceps and chest muscles take center stage during dips, a host of secondary muscles and stabilizers play essential supporting roles. The anterior deltoids, located at the front of the shoulders, are actively involved in shoulder flexion and stabilization throughout the movement.
These muscles help in maintaining proper form and prevent the shoulders from collapsing forward. The core muscles, including the rectus abdominis and obliques, are also significantly engaged. They work to stabilize the torso, ensuring that the body maintains a straight line from head to heels, which is crucial for efficient and safe dip execution.
In addition to the core, the muscles of the upper back, such as the rhomboids and trapezius, contribute to shoulder blade stabilization. This stabilization is vital for maintaining balance and proper posture, particularly during the lowering phase of the dip.
The involvement of these secondary muscles not only enhances overall muscle coordination but also helps in preventing imbalances that could lead to injury over time. Engaging a wide array of muscles during dips provides a comprehensive workout, improving both muscle strength and functional stability.
Integrating dips into a fitness regimen offers a multifaceted approach to upper body development, leveraging the synergistic action of primary and secondary muscles for optimal results.
Variations of Dips and Their Muscle Emphasis
Dips can be adapted in various ways to emphasize different muscle groups. Leaning forward while performing dips increases the engagement of the chest muscles, making the exercise more chest-centric. Conversely, maintaining a more upright posture targets the triceps more directly. Bench dips, executed with hands on a bench and feet on the ground, primarily focus on the triceps and are an excellent option for those who may find traditional parallel bar dips challenging.
Another variation is the ring dip, which involves using gymnastic rings instead of parallel bars. This variation demands greater stabilization, thereby engaging the shoulder and core muscles more intensively. Ring dips also offer an increased range of motion, which can contribute to greater muscle activation.
Weighted dips are another effective variation for those looking to build substantial strength and muscle mass. By adding weights using a dip belt or holding a dumbbell between the legs, one can significantly increase the resistance, thereby intensifying the workout.
Negative dips focus on the lowering phase of the dip. This variation is particularly useful for beginners who are building strength, as it emphasizes controlled descent and muscle engagement without requiring the strength to push back up.
Each of these variations can be strategically incorporated into a workout routine to target specific muscles and achieve diverse fitness goals.
Proper Form and Technique to Maximize Muscle Engagement
Proper form and technique are crucial for maximizing muscle engagement during dips. Start by gripping the parallel bars or bench with your hands shoulder-width apart, and lift your body by extending your arms. Lower your body in a controlled manner by bending your elbows until your upper arms are parallel to the ground.
Keep your elbows close to your body to avoid unnecessary stress on the shoulder joints. Throughout the movement, engage your core to maintain a straight line from your head to your heels. Ensure your shoulder blades are retracted and avoid allowing them to collapse forward. This will help maintain proper posture and enhance muscle activation.
Avoid locking out your elbows at the top of the movement to keep constant tension on the muscles. If you’re using variations like ring dips or weighted dips, the same principles apply, with additional focus on maintaining stability and control. Practicing proper form not only optimizes muscle engagement but also helps prevent injuries, allowing for more effective and safer workouts.
Incorporating Dips Into Your Workout Routine
Incorporating dips into a workout routine can significantly enhance upper body strength and muscle definition. For those focusing on upper body development, dips can serve as a key component of a push workout, effectively complementing other compound movements like bench presses or push-ups. To maximize their benefits, it’s essential to tailor the variations and intensity of dips to one’s fitness level and goals.
Beginners may find starting with bench dips more manageable, gradually progressing to parallel bar dips as strength and confidence increase. For more advanced individuals, incorporating weighted dips can add a challenging element to the routine, promoting greater muscle hypertrophy and strength gains.
Dips can also be utilized as a finishing exercise to thoroughly fatigue the triceps and chest muscles after completing other upper body exercises. This approach ensures comprehensive muscle activation and can aid in achieving balanced muscle development.
Additionally, varying the type of dips performed can prevent workout monotony and target muscles differently. For instance, ring dips demand greater stabilization and core engagement, offering a distinct challenge compared to traditional dips. Integrating different dip variations keeps the muscles guessing and can lead to more balanced strength and muscle growth.
Ultimately, the versatility of dips makes them an invaluable addition to any workout regimen, whether one is a beginner looking to build foundational strength or an advanced athlete aiming for peak muscle development.
Hopefully this article helped you understand what muscles dips work.